PC-7 Team
Country
Switzerland
Size
9 Aircraft
Base
Dübendorf Air Base
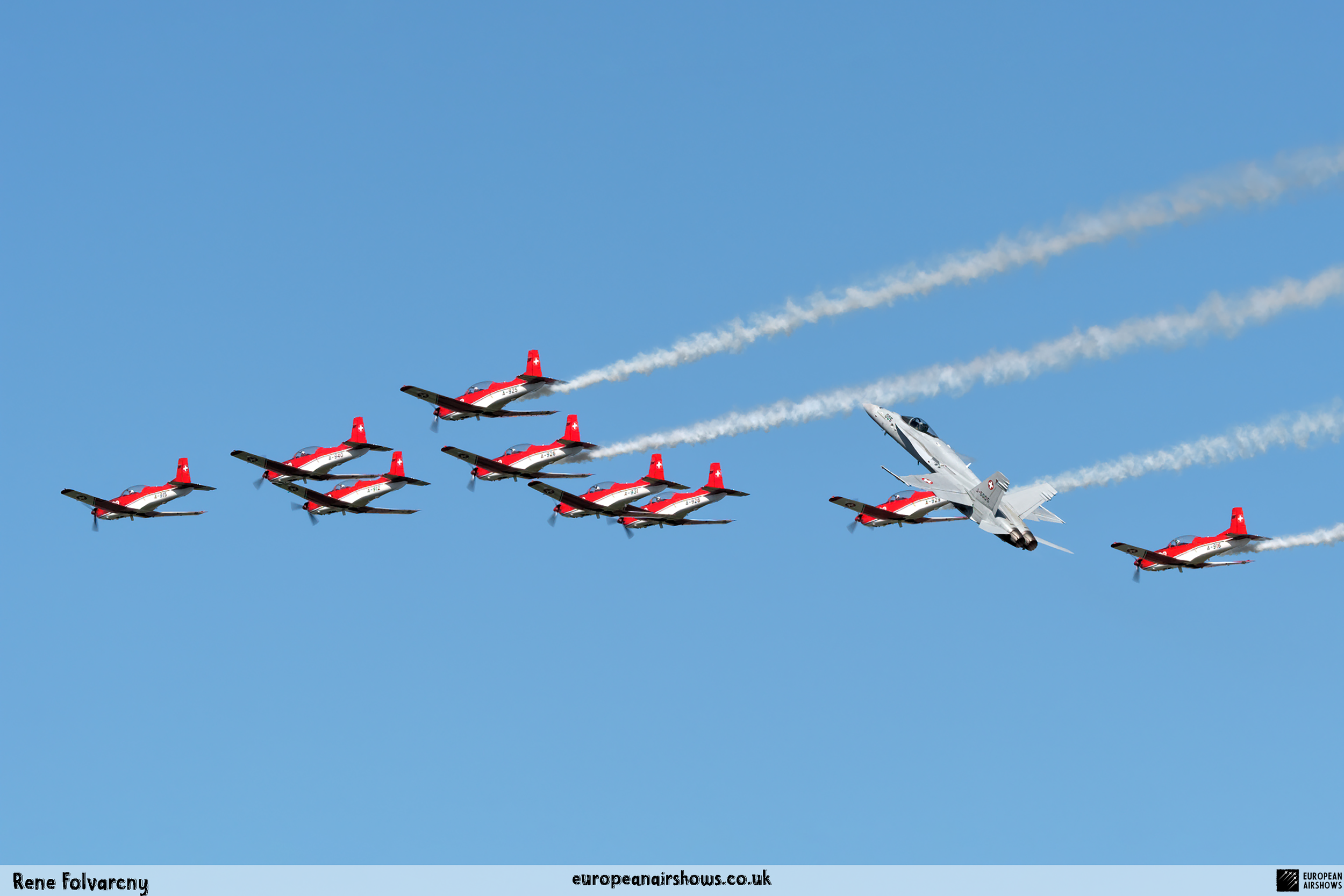
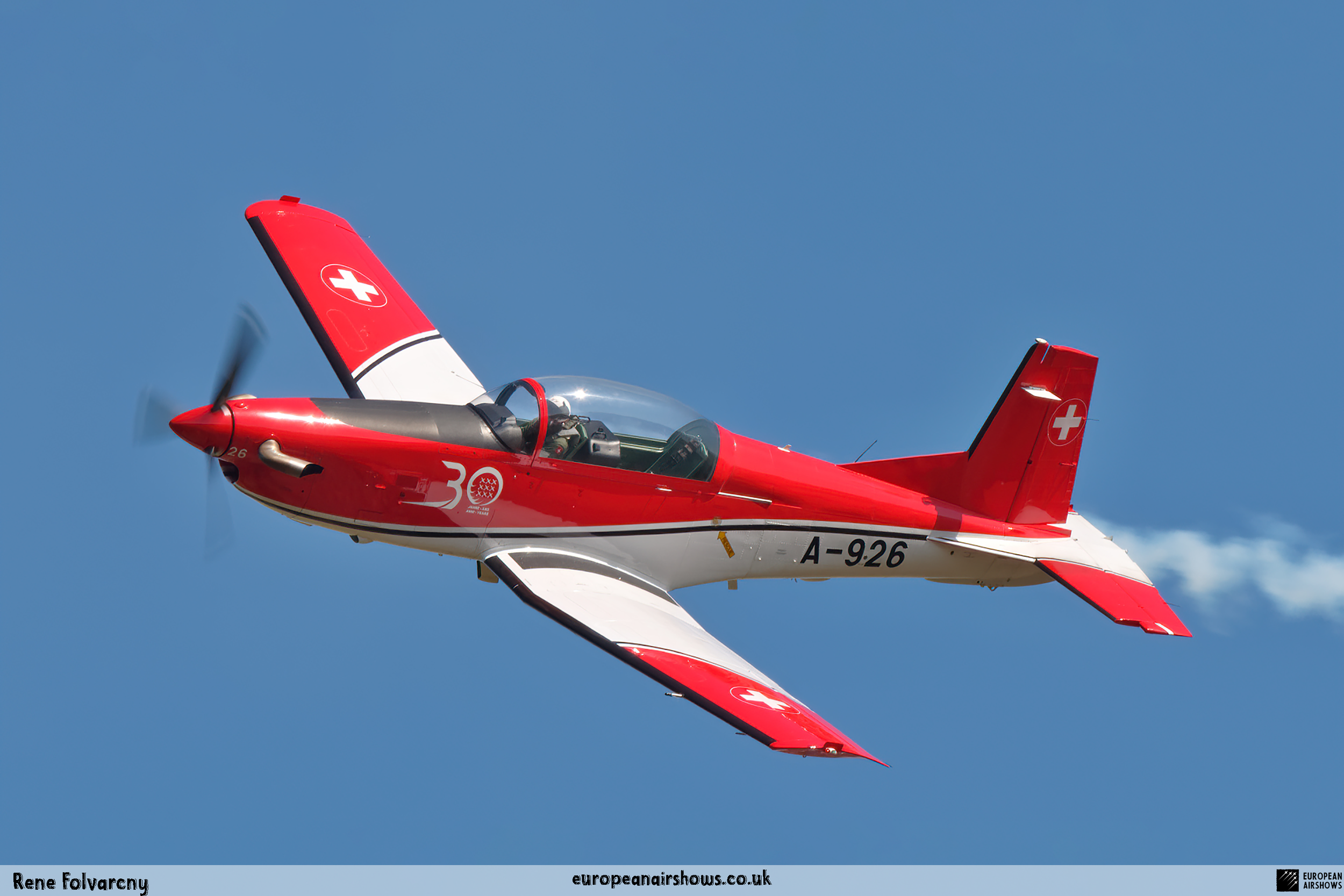
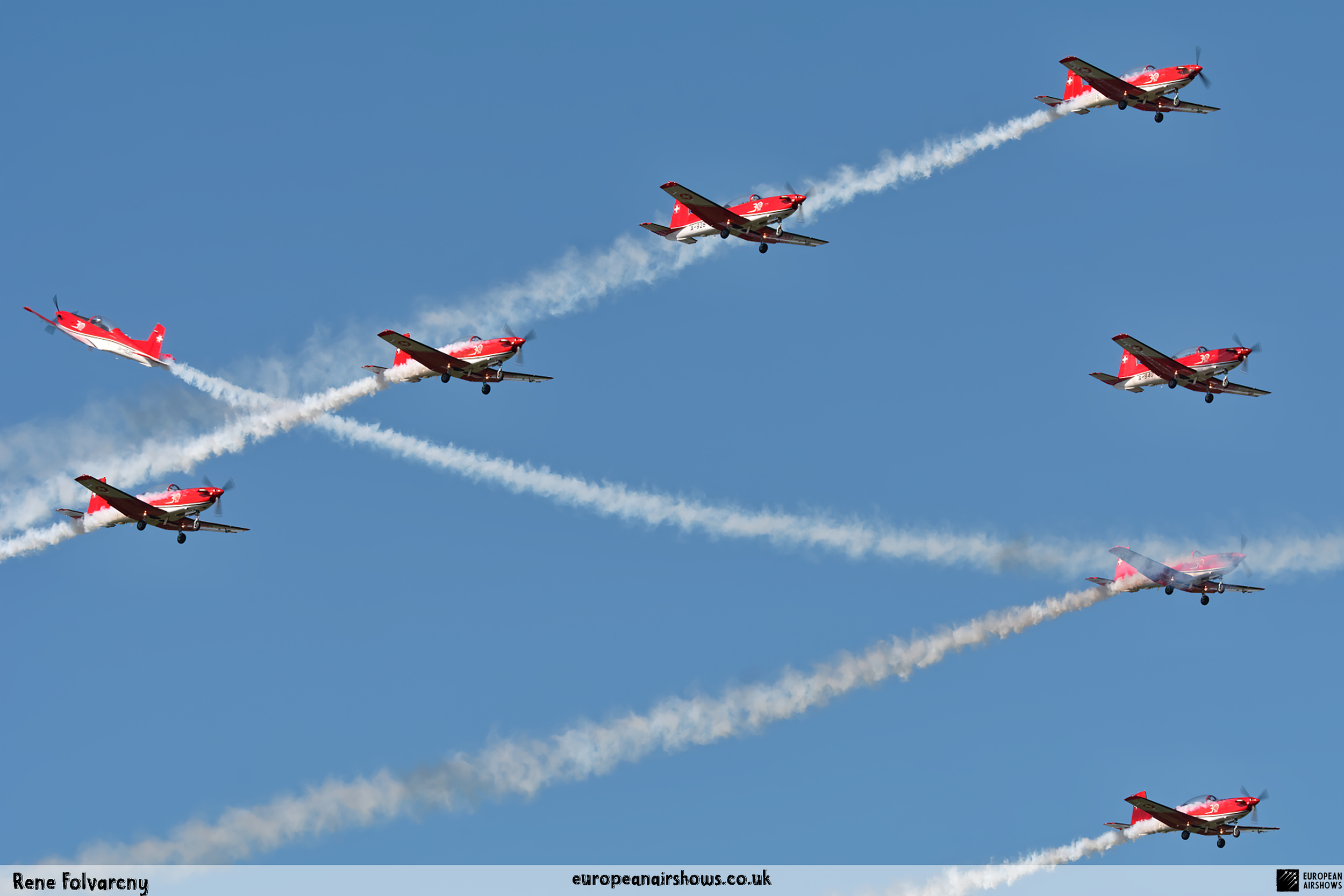
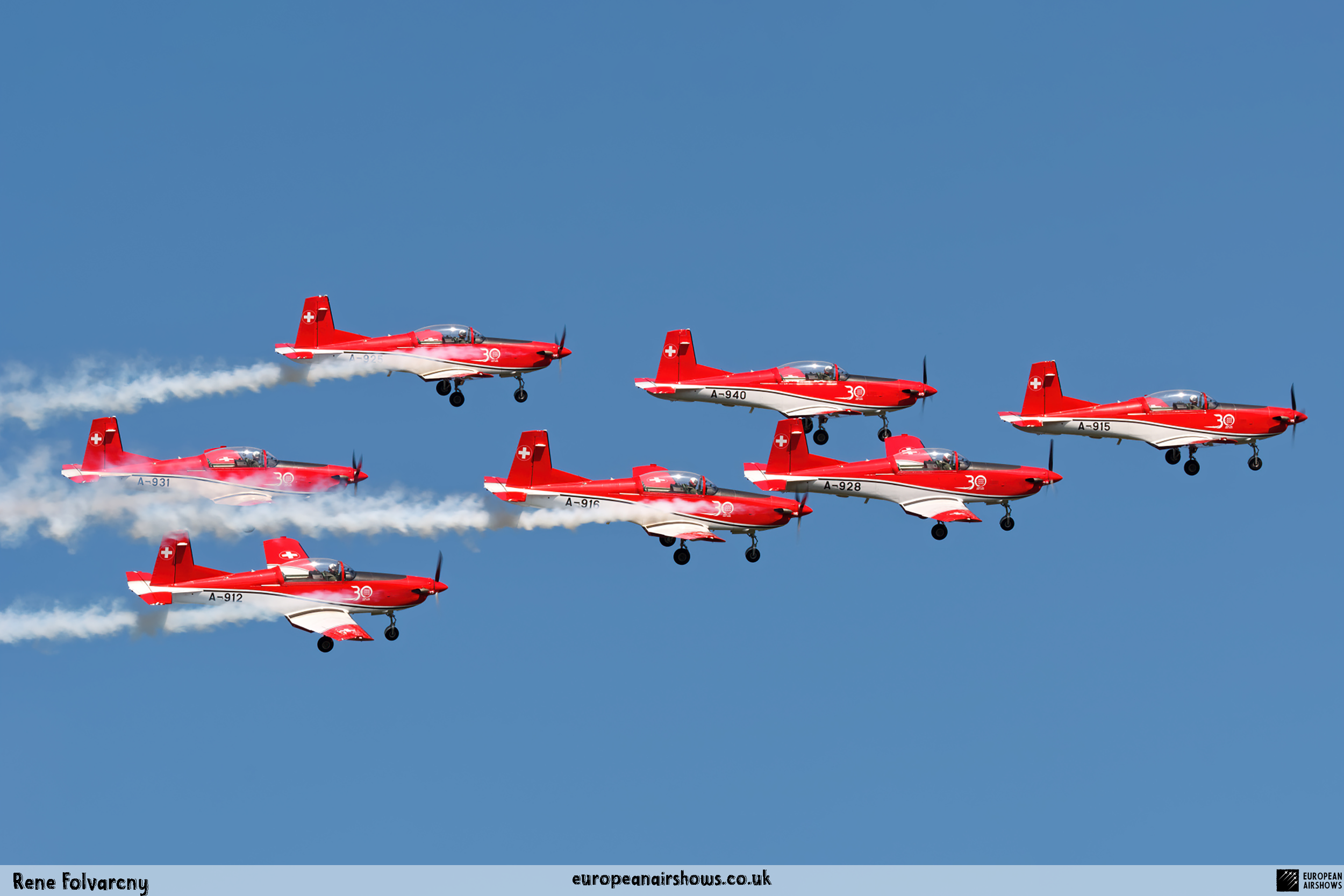
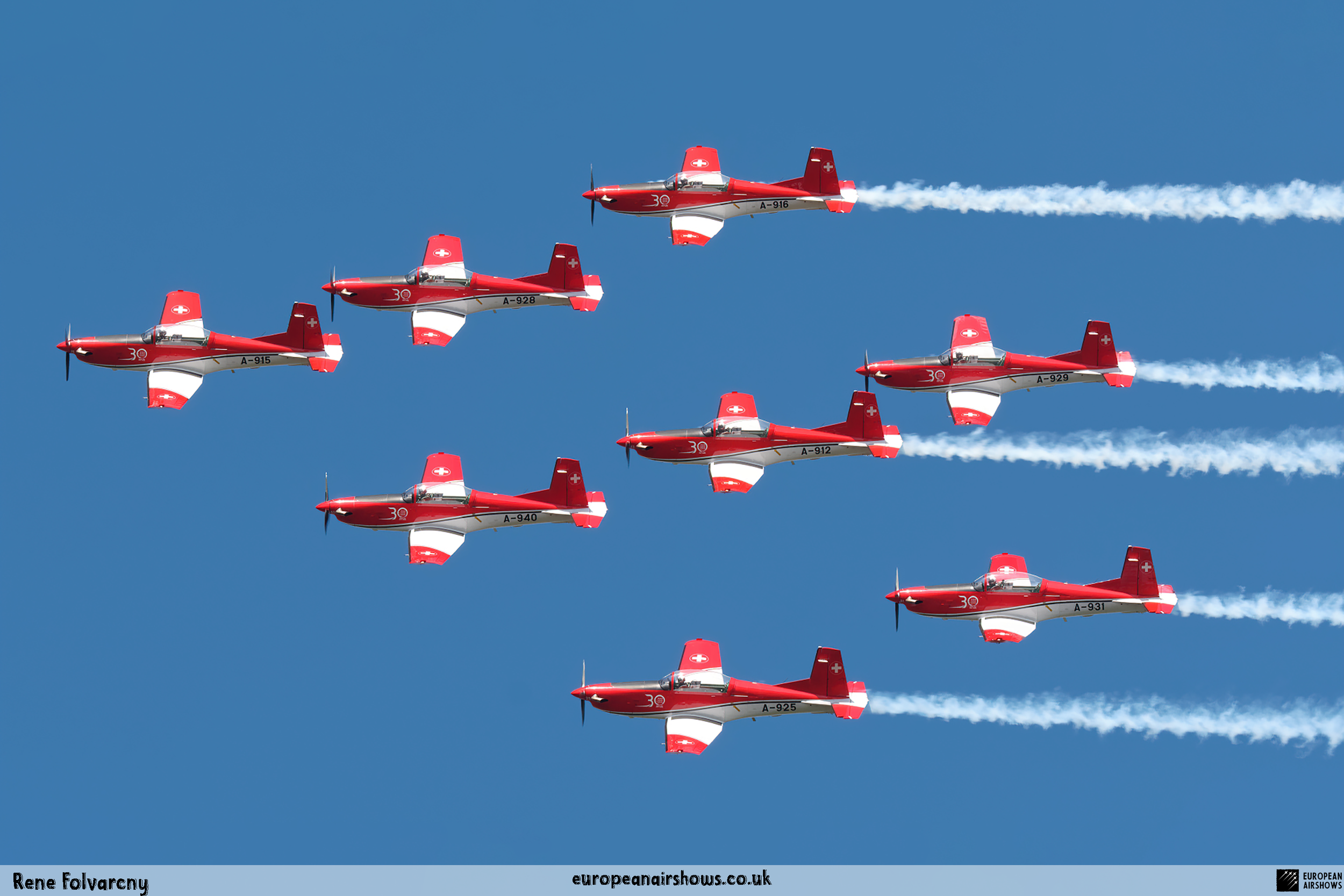
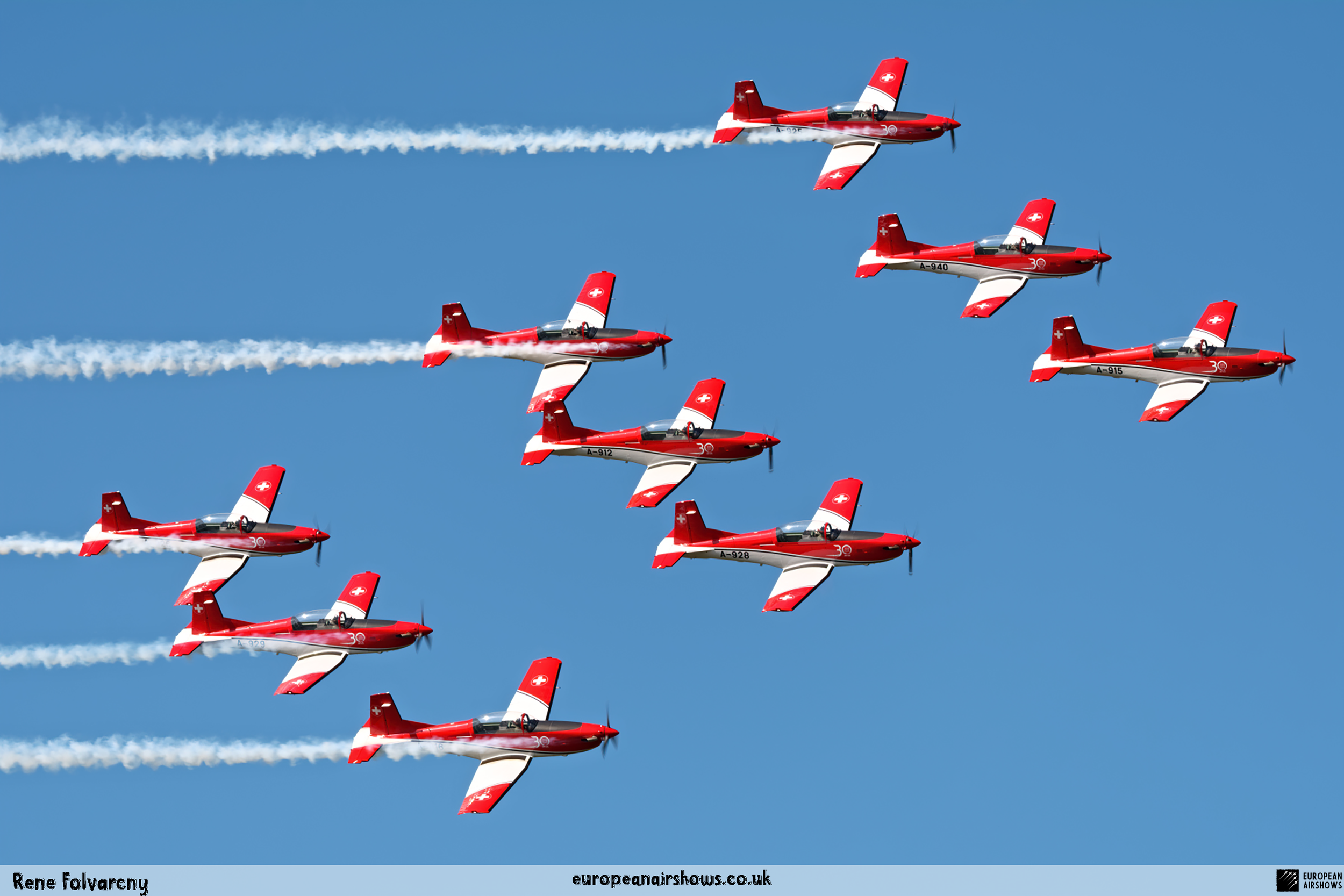
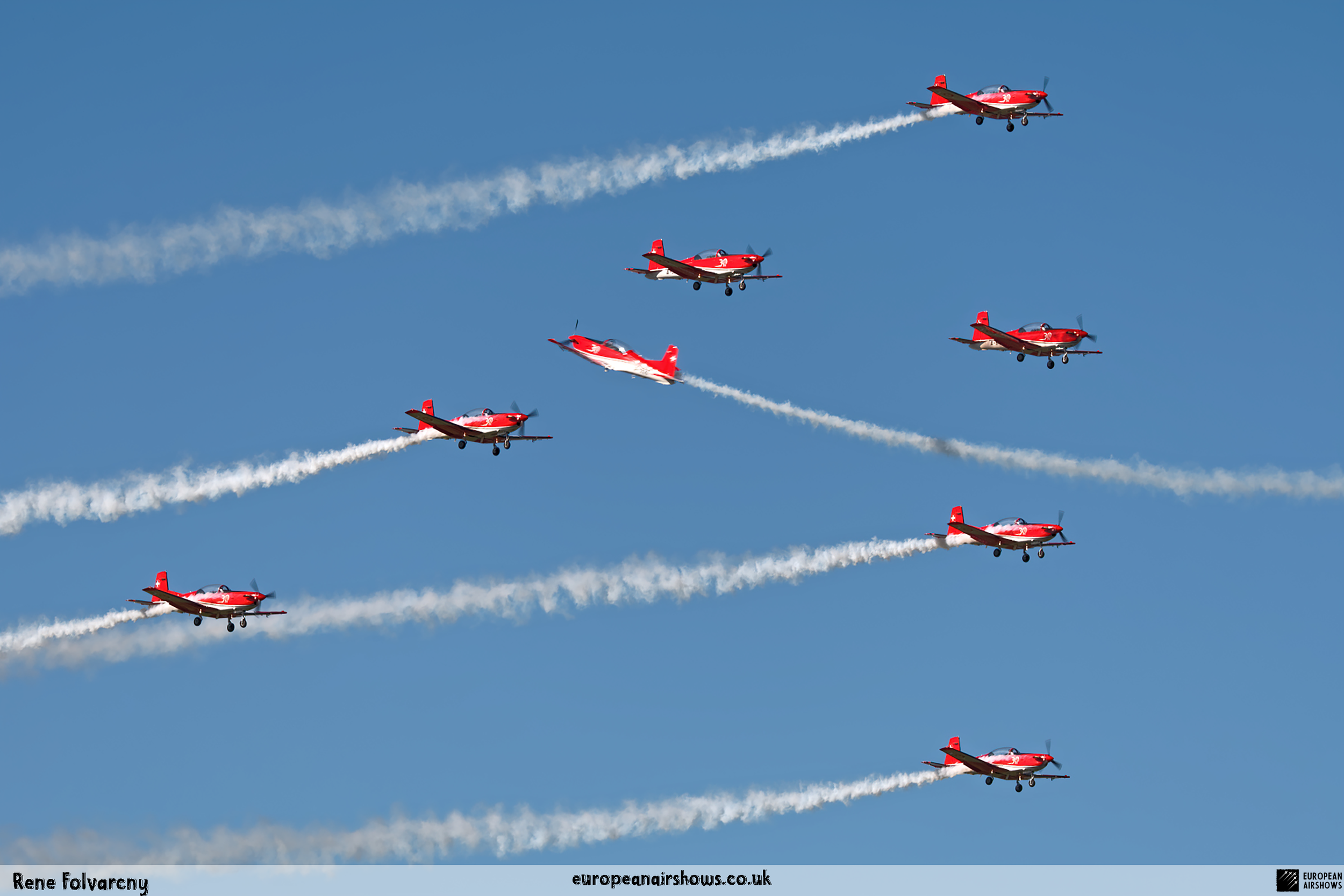
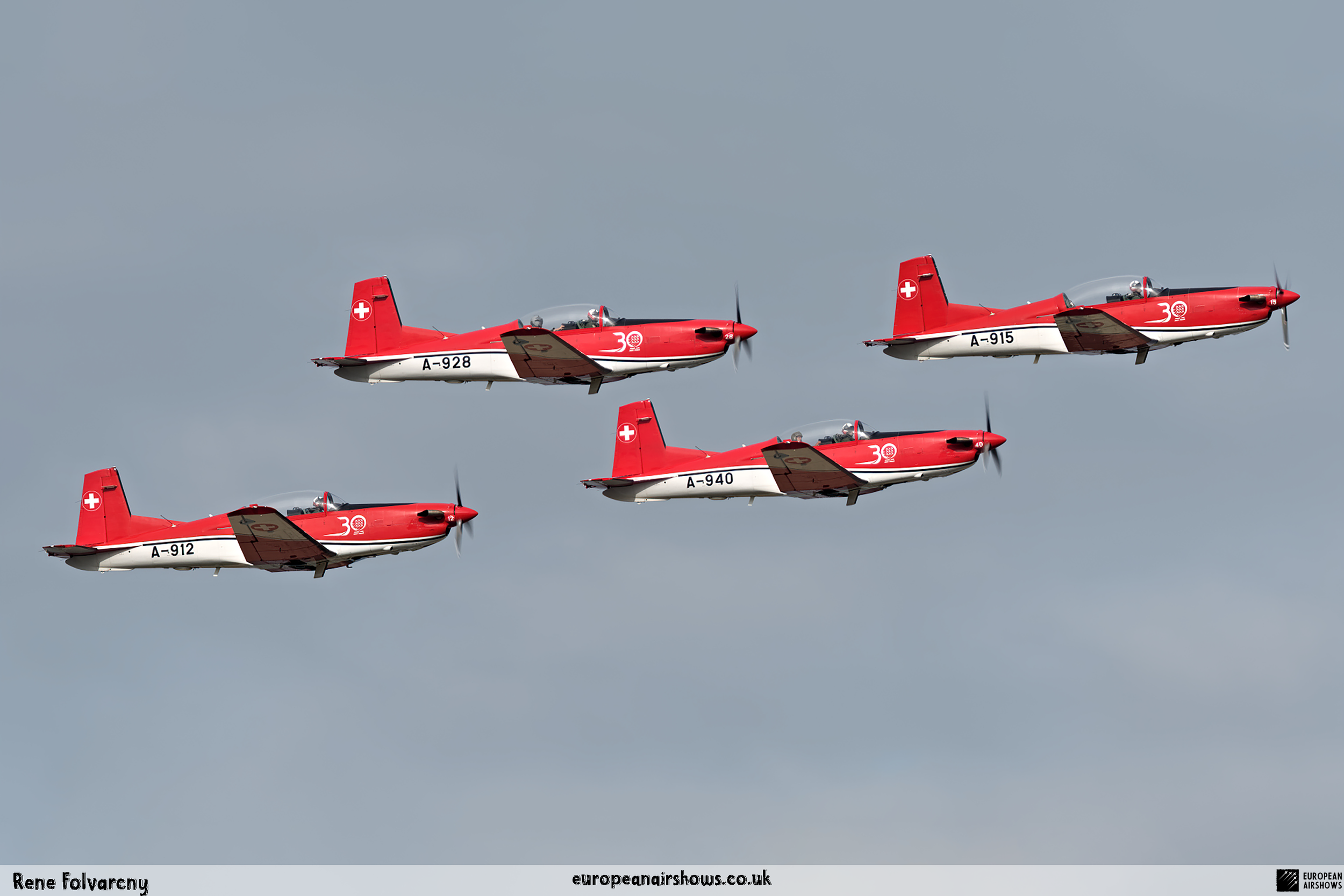
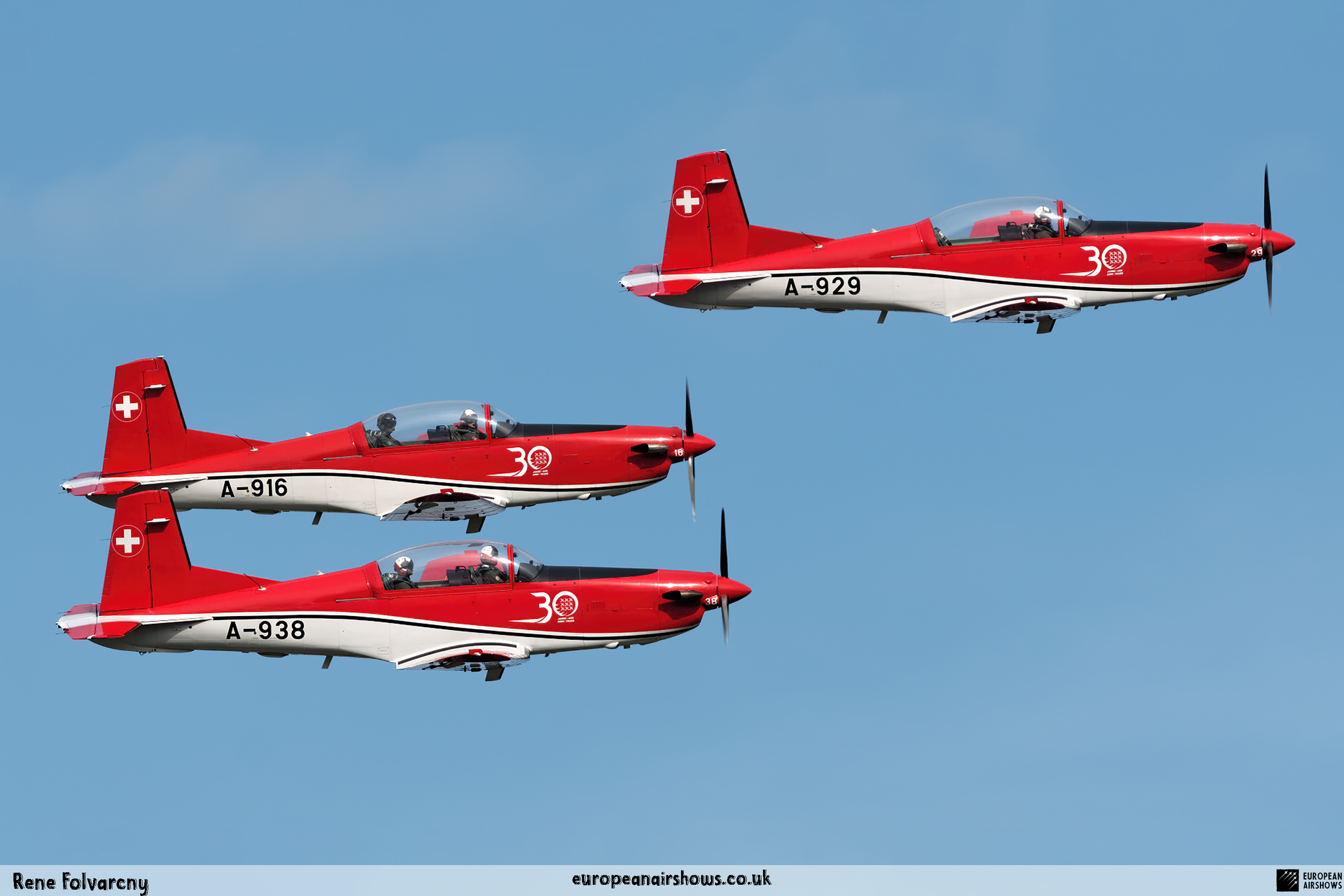
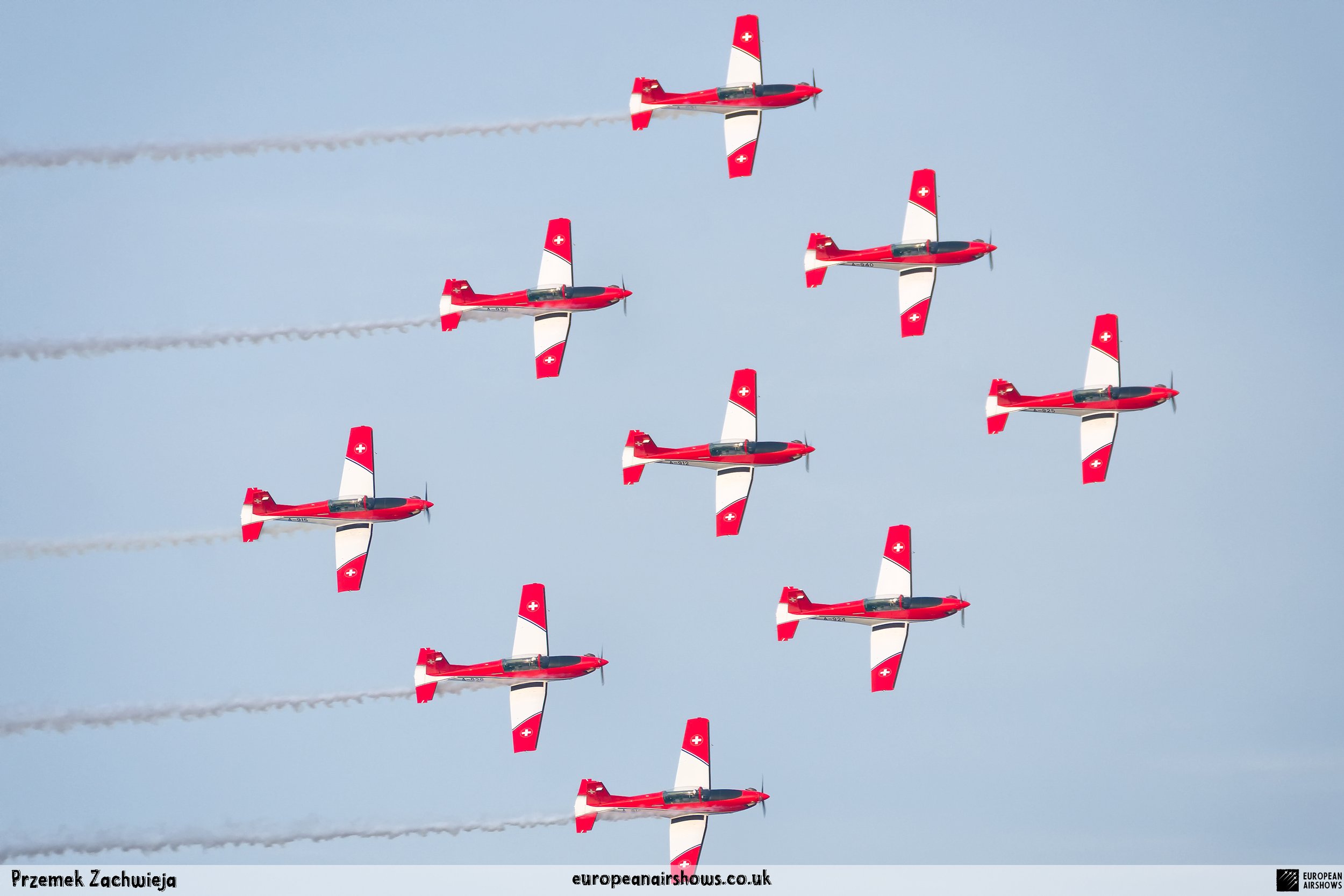
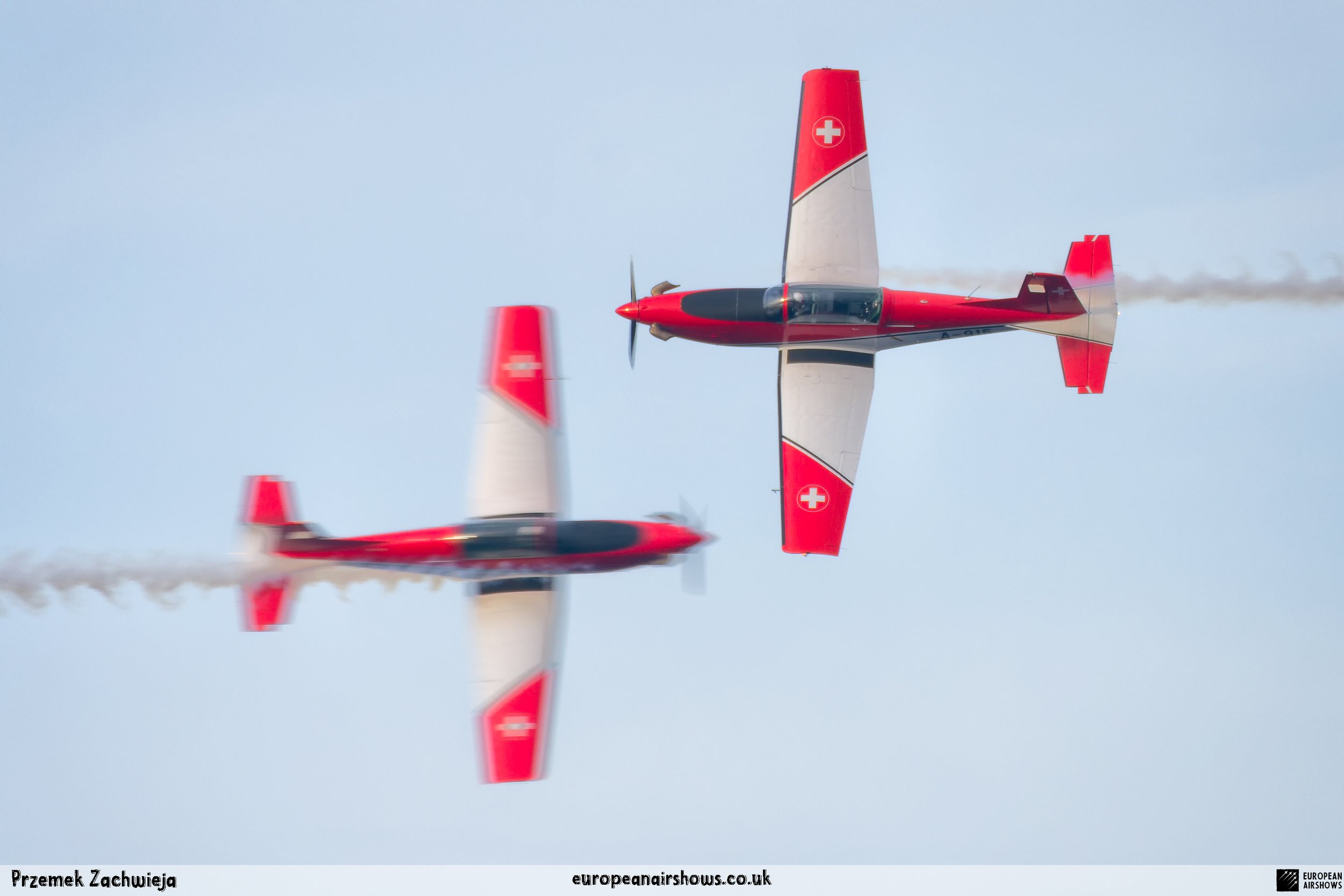
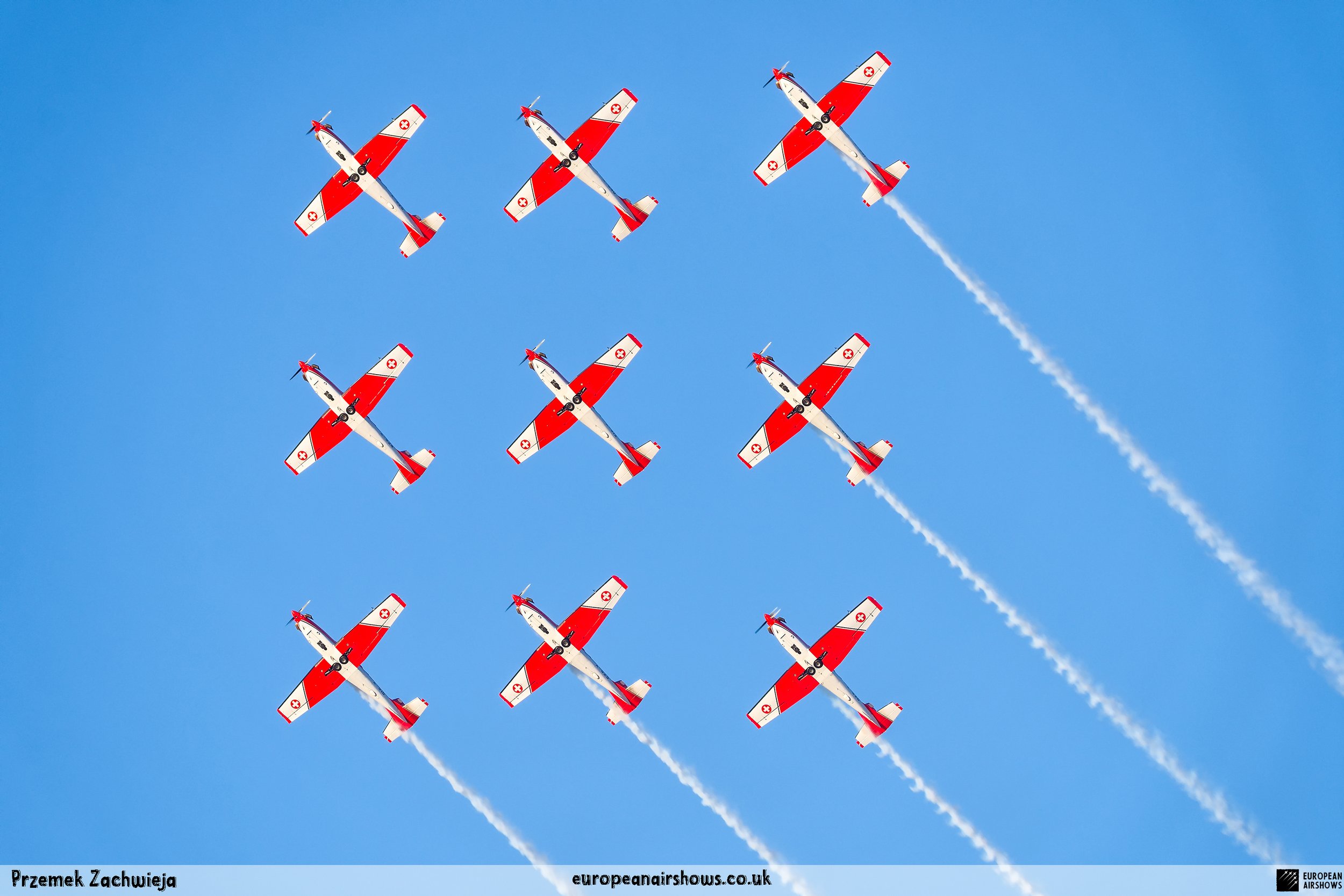
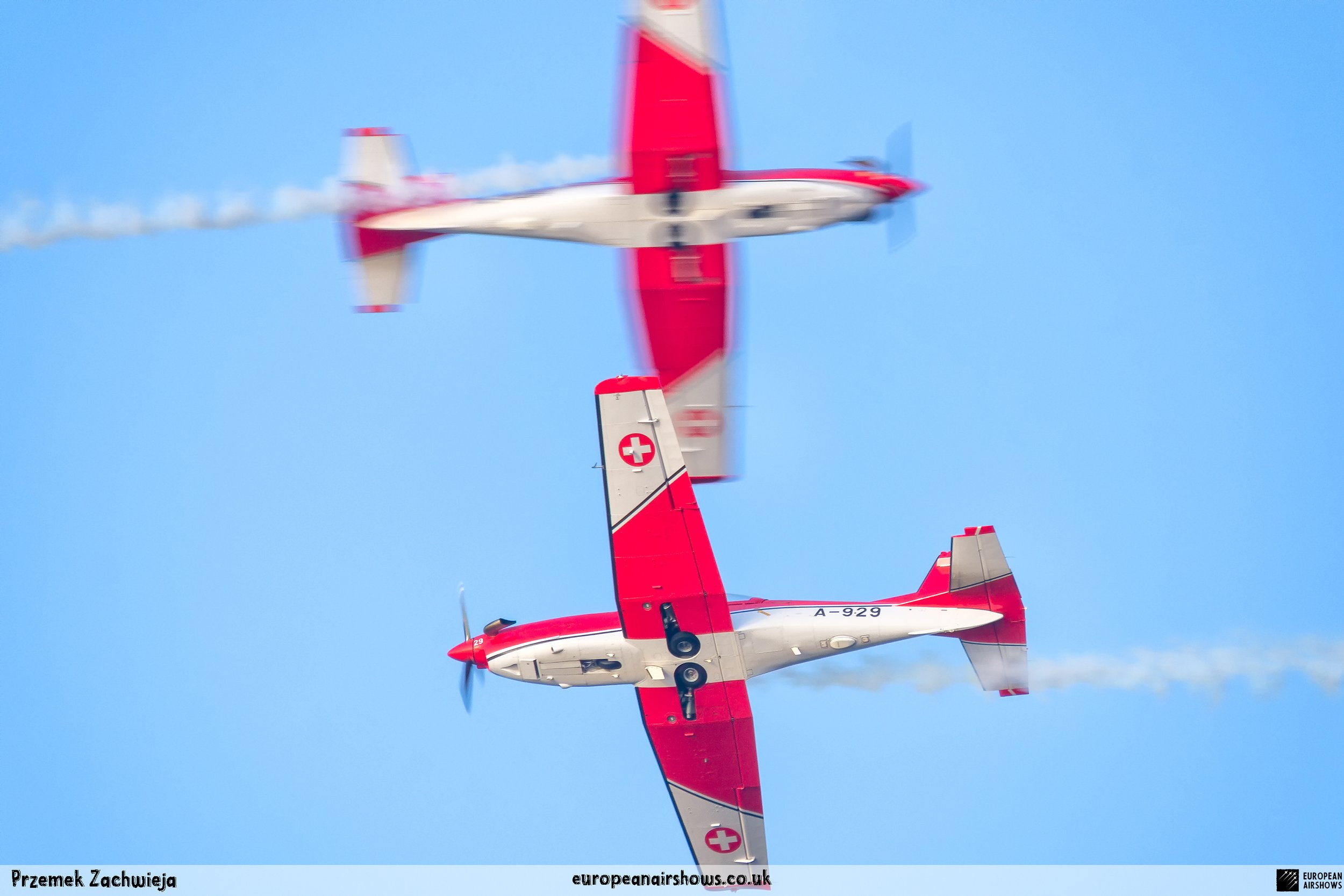
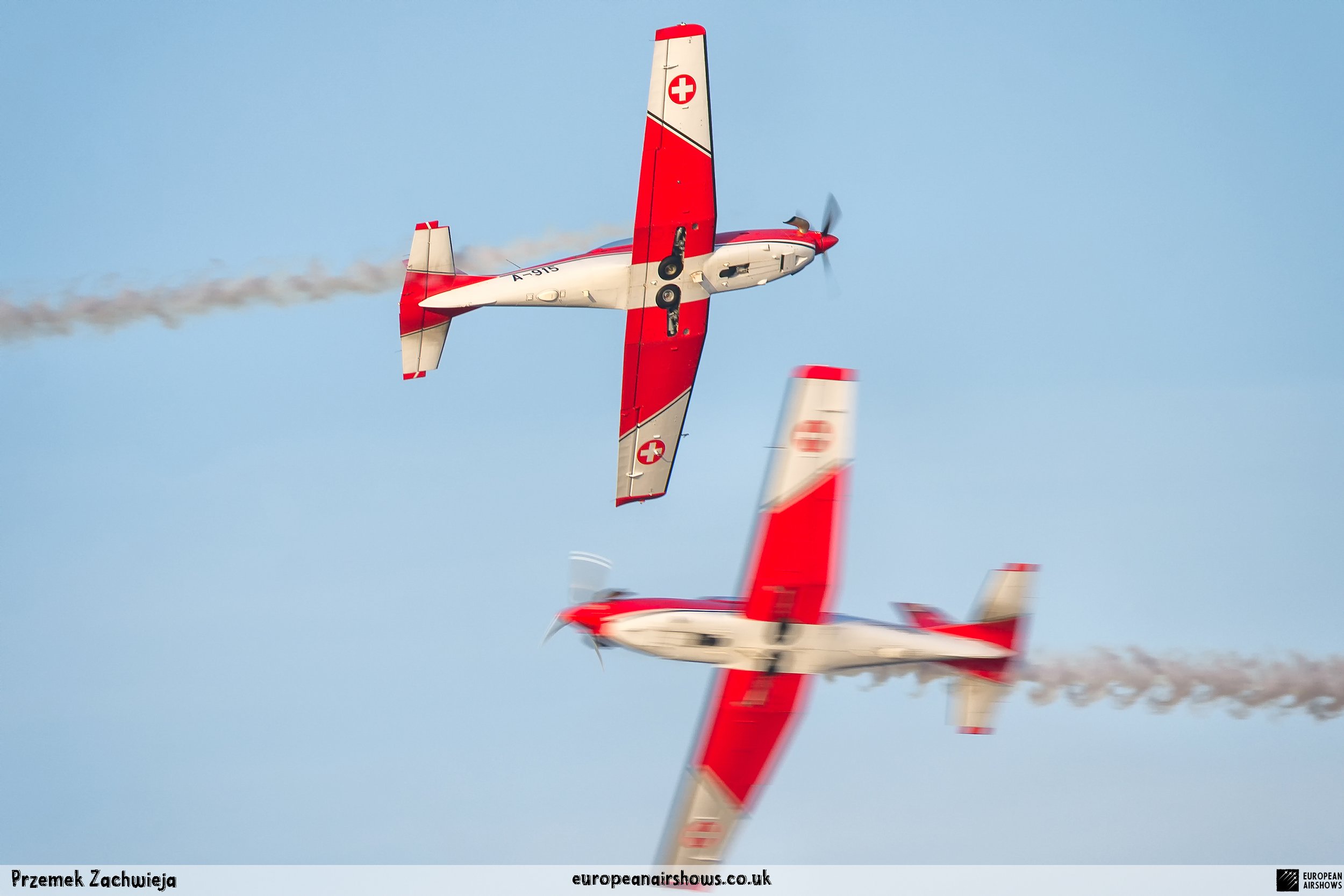
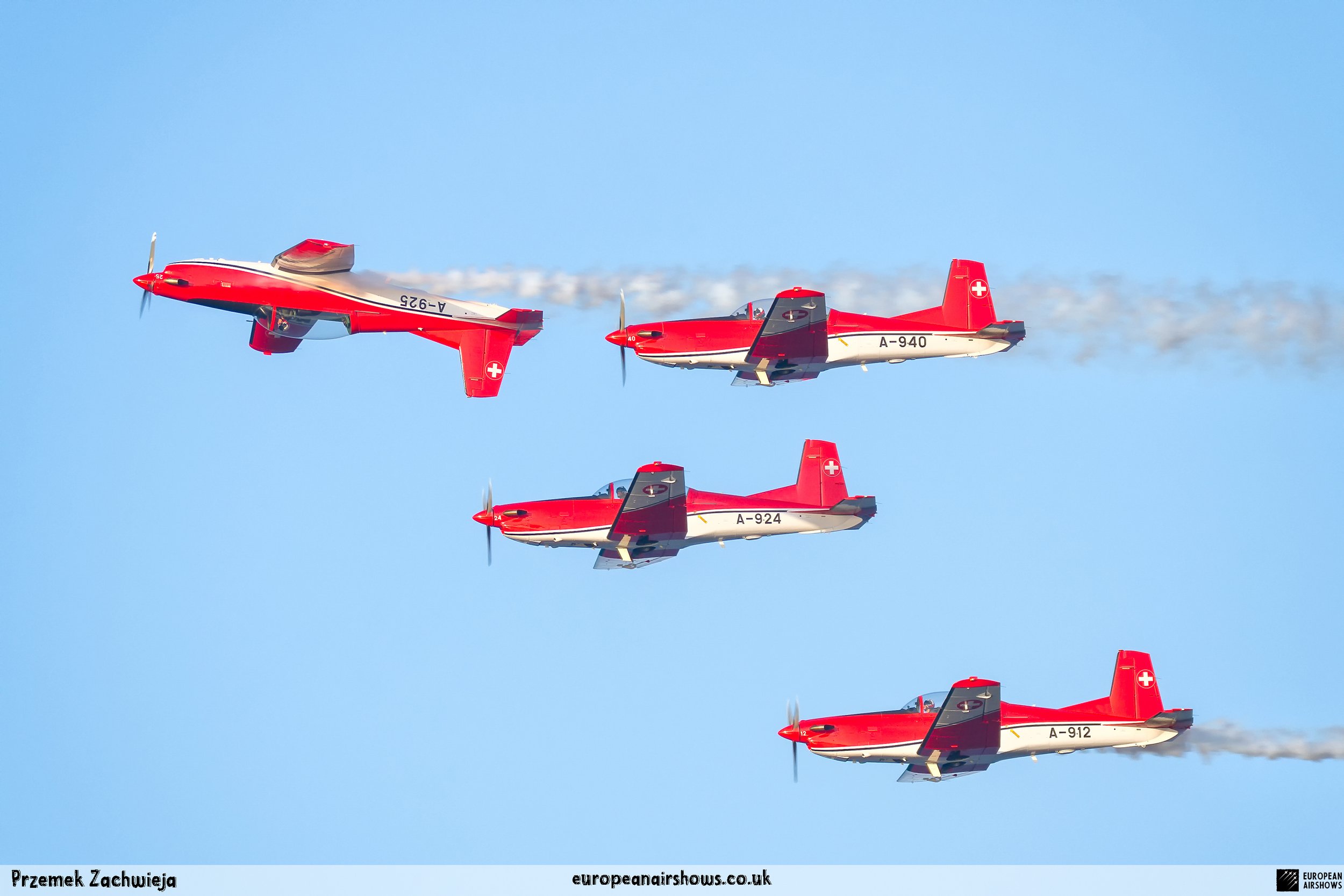
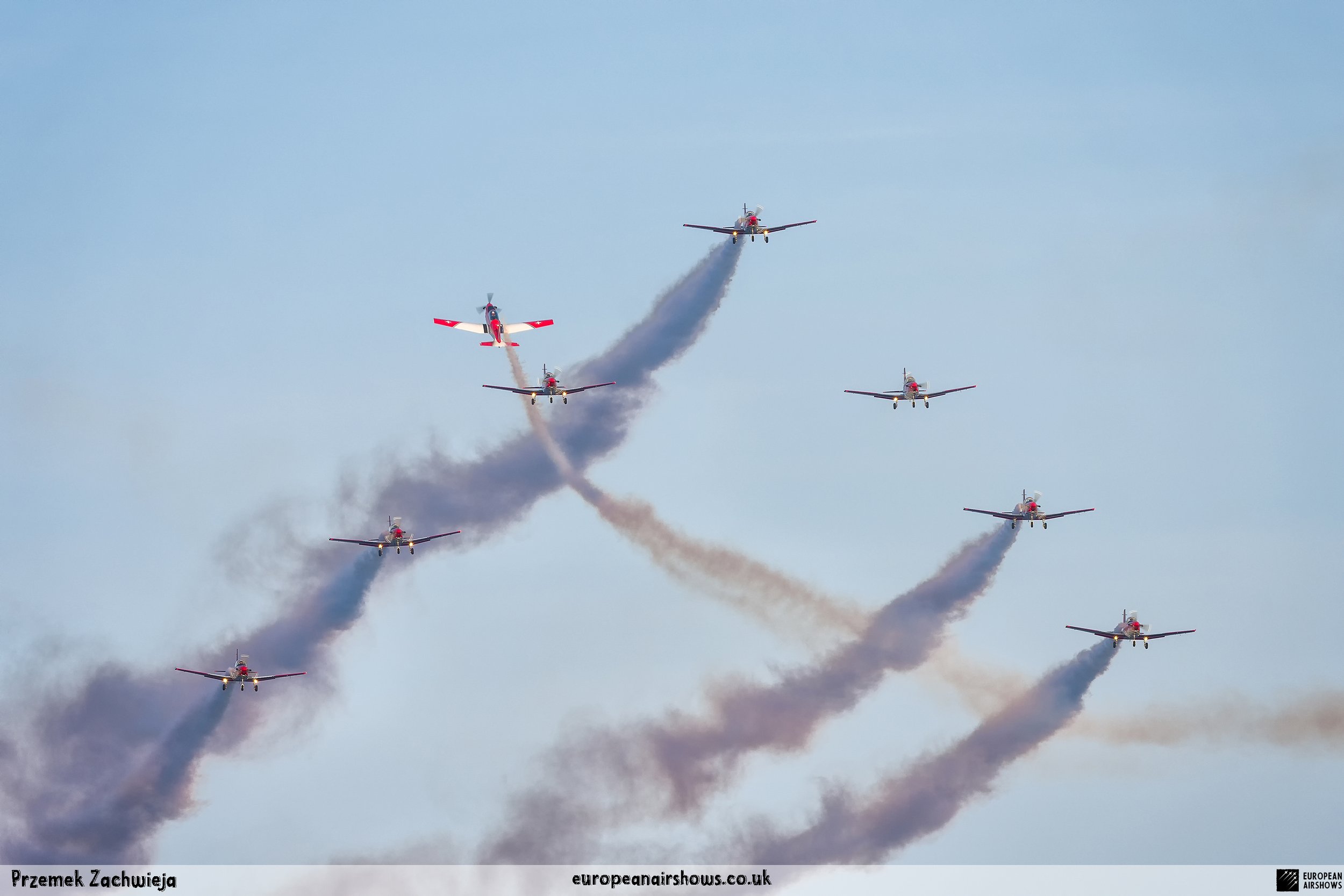
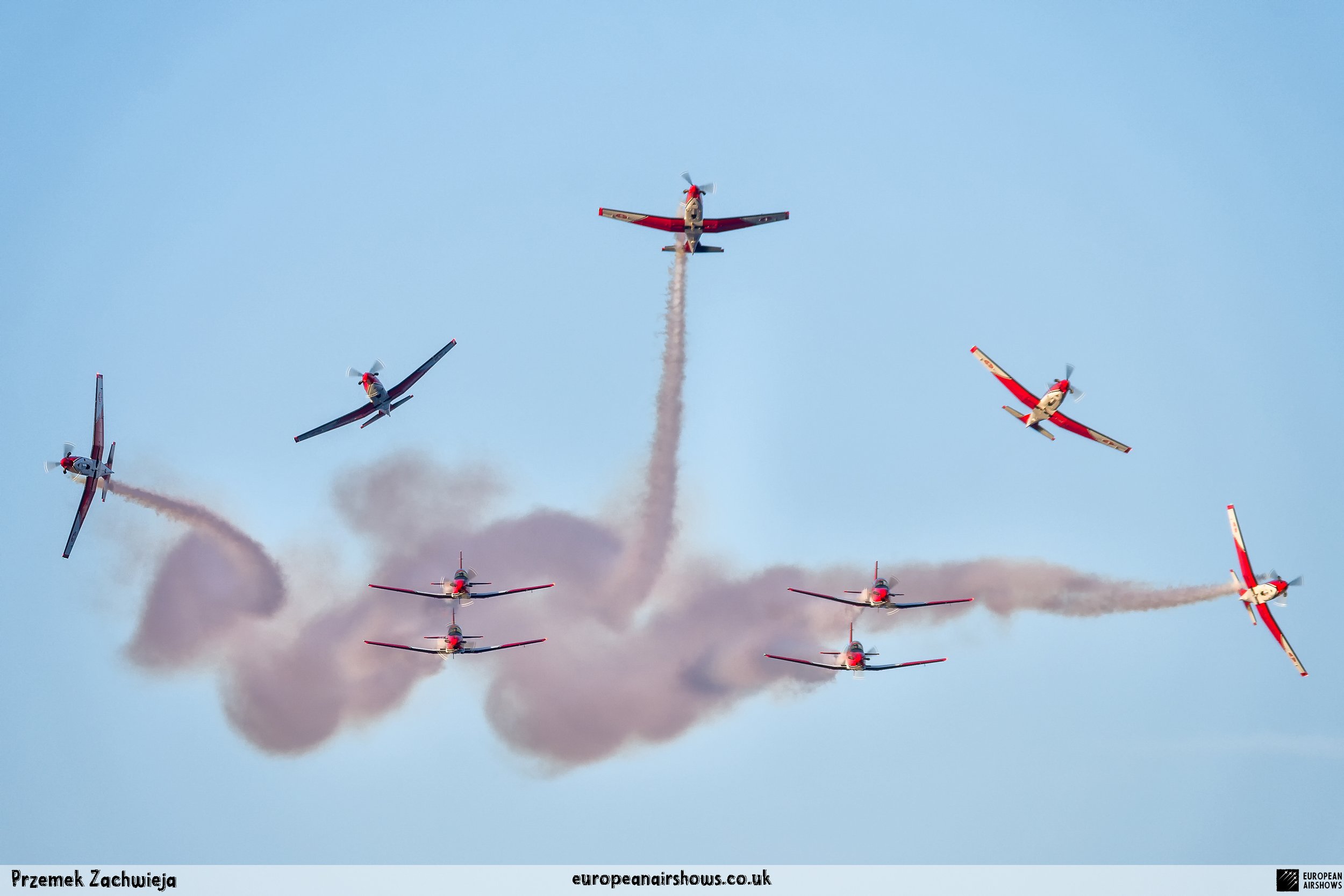
The "PC-7 TEAM" is the second aerobatic display team of the Swiss Air Force. The team consists of ten Pilatus PC-7 turboprop trainers, nine display pilots, a single spare pilot, two commentators, the commander of the team and a number of technicians. The team's pilots each use "Turbo" call signs followed by their number. All the PC-7 aircraft are painted in an overall red and white paint scheme and are equipped with smoke generators. The PC-7 TEAM initially practices for 2 weeks in the spring and then once or twice before each show, normally on the day before the actual show.
History
Soon after the PC-7 was introduced in 1982, the Swiss Air Force started to present the new aeroplane in solo displays. The first public team display was in 1987, performed by an ad-hoc team of nine volunteer pilots. When the Swiss Air Force celebrated its 75th anniversary in 1989, the PC-7 Team was officially established. Since then, it has been performing in Switzerland several times a year, and since 1992 also regularly abroad.
Since its establishment, the team has flown the Pilatus PC-7 Turbo Trainer. In October 2006, it was replaced by the NCPC-7, which is a PC-7 equipped with a new cockpit. The PC-7 Team currently performs displays on nine Pilatus PC-7 aircraft in the standard configuration of the Swiss Air Force's PC-7s making it the largest turboprop aerobatic team in the world. The PC-7 Team still uses the unique Swiss Air Force Bambini-Code for its radio communication. Until the end of 2007, the team's PC-7 aircraft were painted in an orange and aluminium paint scheme. Then in 2008, the team's aircraft received a new paint scheme of overall red and white.
Since it’s creation, the team displayed at a number of European airshows and won a number of different awards such as the King Hussein Memorial Sword at the Royal International Air Tattoo UK.
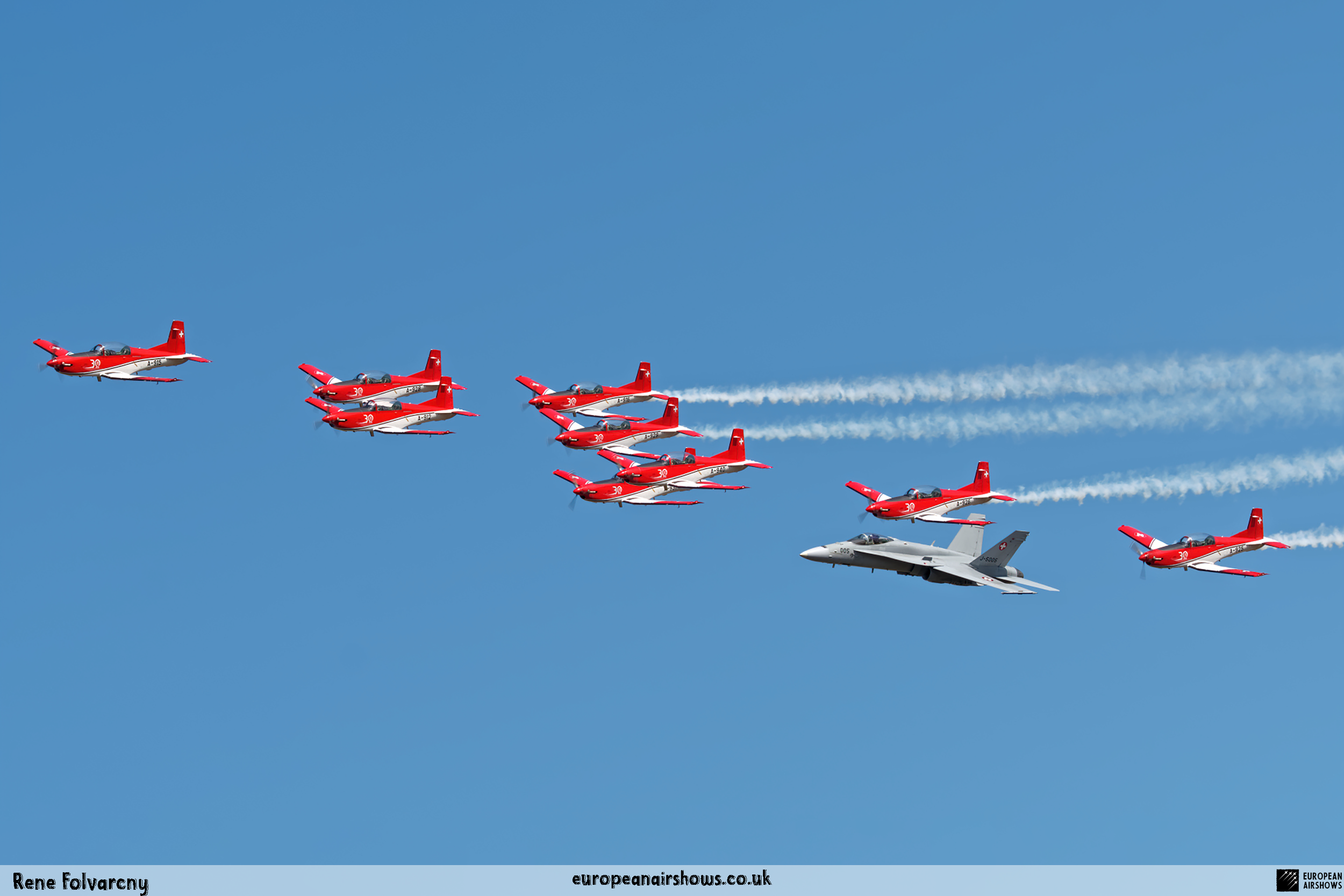
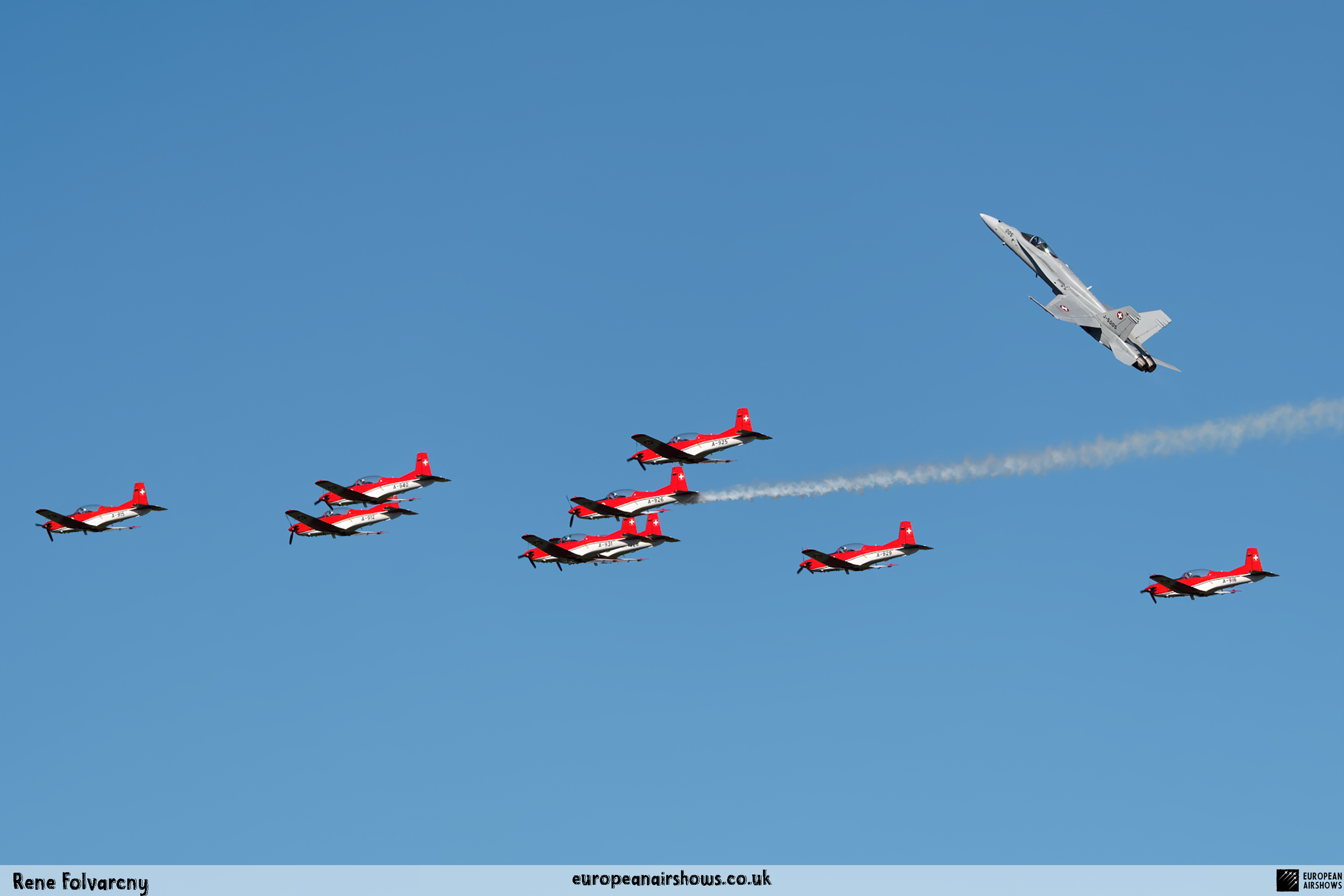
The PC-7 Team's homebase is Dübendorf Air Base, but they often operate from Militärflugplatz Emmen or Locarno Airport. All pilots of the PC-7 Team are full-time military pilots and usually fly the F/A-18. The display routine is made up of 23 different elements. In 2014 the nine aircraft were fitted with smoke generators, it was publicly used for the first time on the 1st of August 2014 at Buochs Airport at the roll-out of the Pilatus PC-24. The smoke system was built and financed by the company Pilatus Aircraft. Currently, seven smoking systems are available which can be mounted in the luggage compartment of the PC-7. The diesel-oil mixture is injected into the right exhaust of the PC-7. For large airshows like RIAT or the Air14, the PC-7 Team flies in the opening of the flight demonstration also often with the Patrouille Suisse, the Hornet Solo Display Team or the Super Puma Display Team in a joint flyover formation.
On September 7, 2014, at the Air14 Air Show in Payerne PC-7 Team performed a unique flight demonstration together with the Patrouille Suisse with a total of 15 aircraft.
| Back to Top |
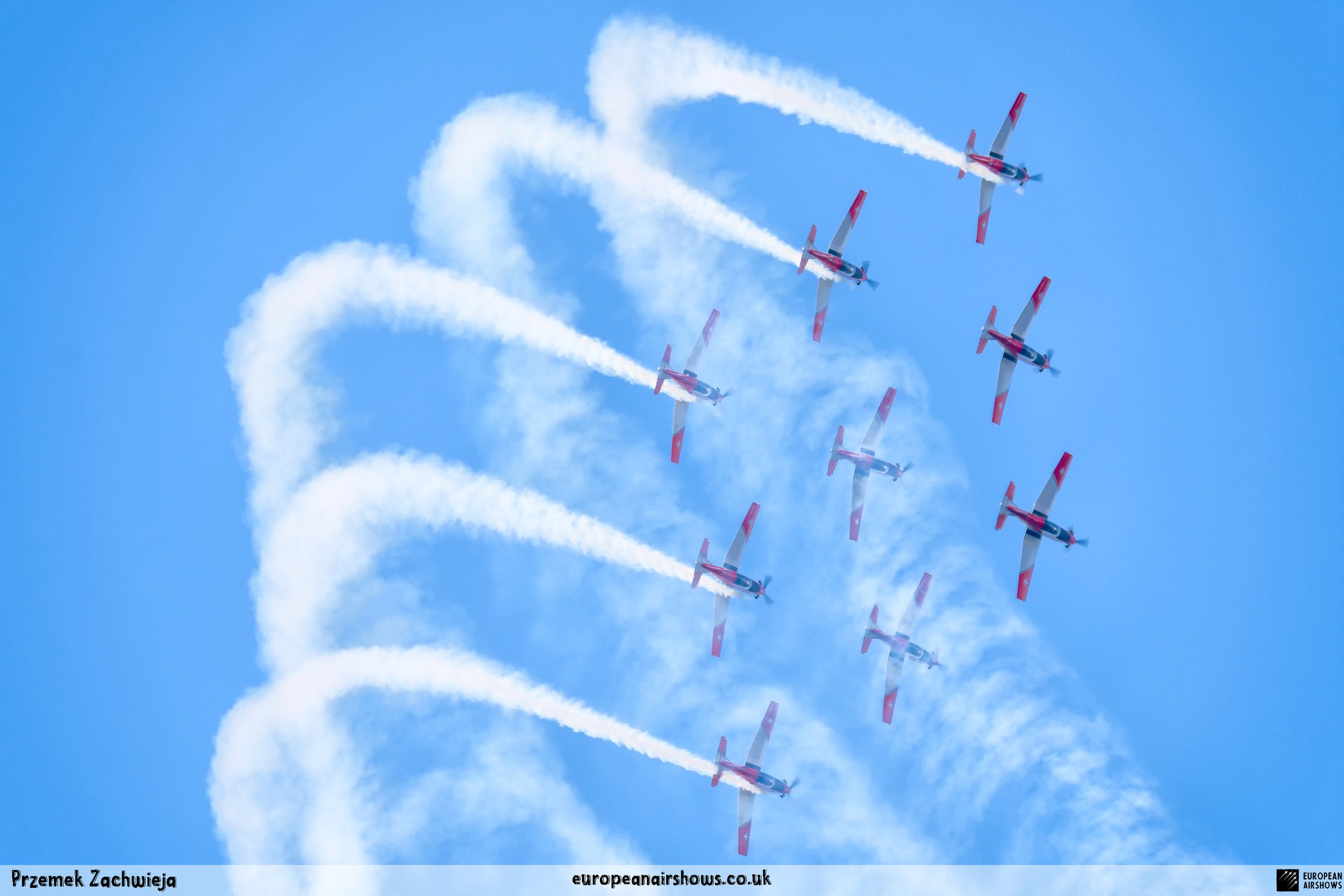
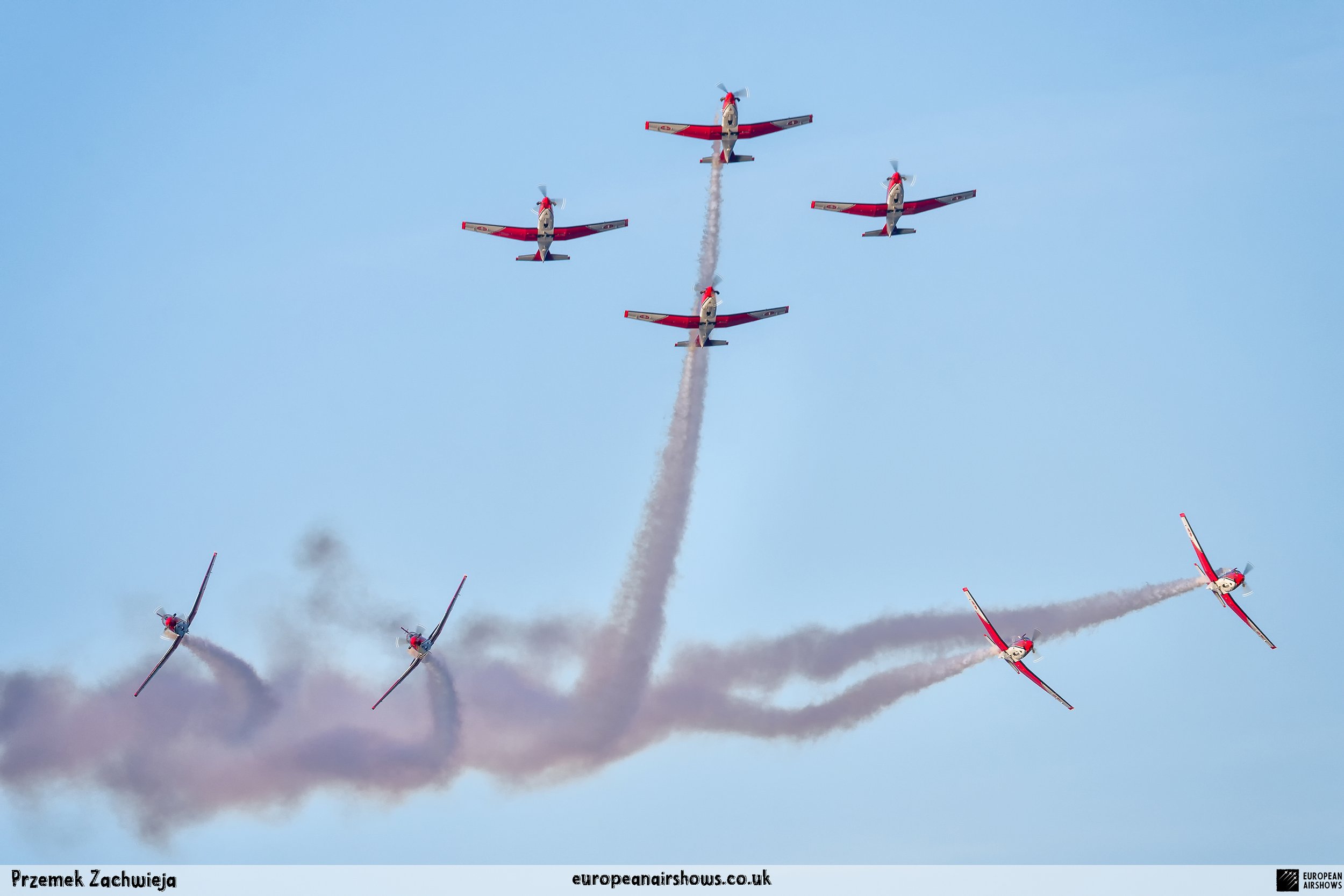
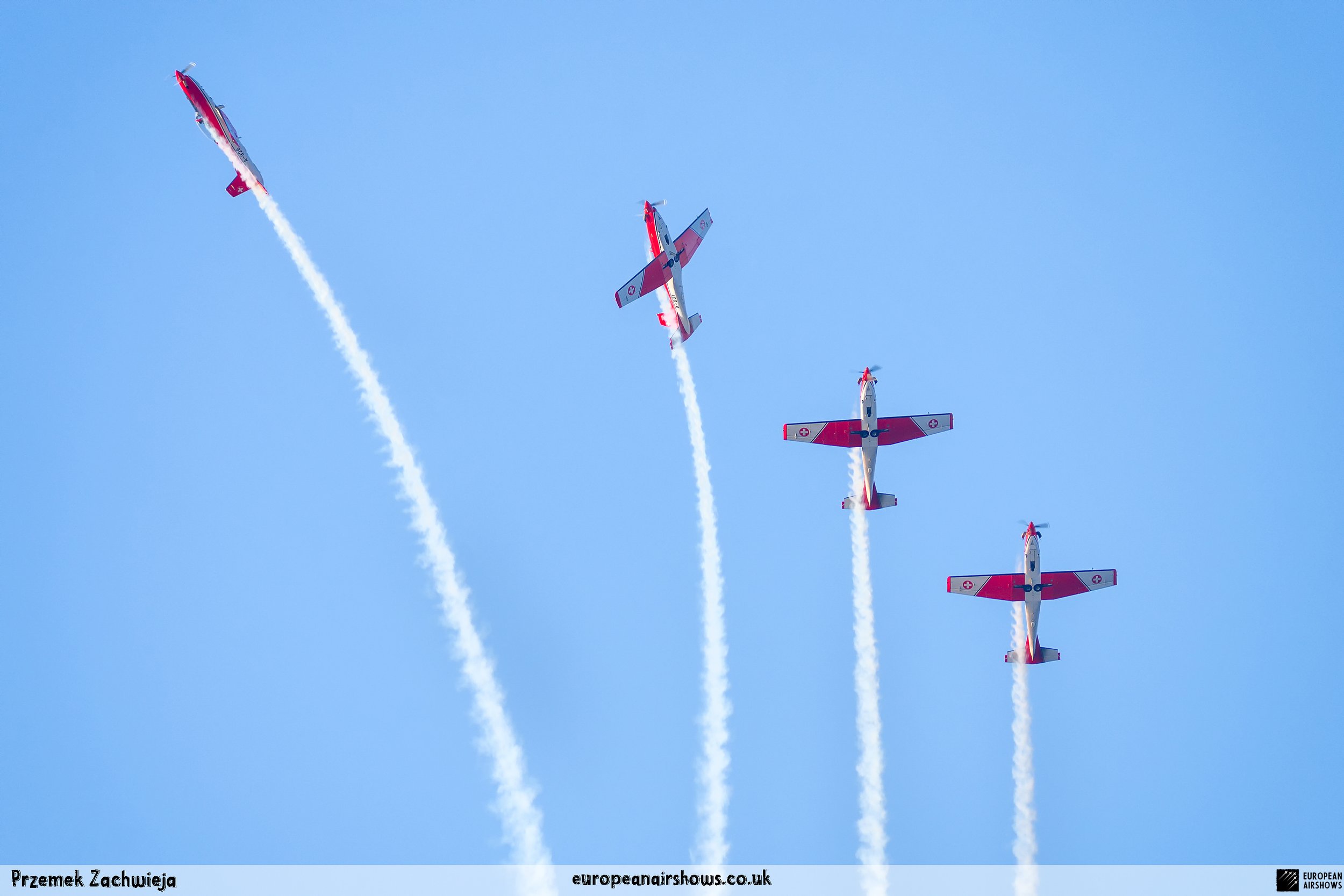
Signature Formations
Apollo
Doppel-Diamant
Losange
| Back to Top |
Pilatus NCPC-7 Turbo Trainer
The Pilatus PC-7 Turbo Trainer is a low-wing tandem-seat training aircraft designed and manufactured by Pilatus Aircraft of Switzerland. The aircraft is capable of all basic training functions including aerobatics, instrument, tactical and night flying.
The PC-7 was developed from the preceding Pilatus P-3, largely differing by the adoption of a turboprop engine, a bubble canopy, and a new one-piece wing. Introduced during the 1970s, it has since developed a sizable presence in the global trainer market. The type has been adopted by in excess of 20 air forces as their ab initio trainer, as well as multiple civilian operators. Over one million hours have reportedly been flown by PC-7s worldwide. In addition to training operations, some aircraft are armed and have been used for combat missions by several customers, including Chad, Iran, and Mexico, often in violation of the relevant export agreement between the customer and the Swiss government.
An improved model of the aircraft, the PC-7 Mk II, was developed during the 1990s by combining the newer PC-9's airframe and avionics with the PC-7's smaller turbine engine. Reportedly, in excess of 500 PC-7s have been sold to various operators, the majority of which still being in service. In Pilatus' line-up, the PC-7 has been succeeded by the newer PC-9 and PC-21 trainers.
Work on what would become the PC-7 commenced during the 1960s. It was based on the earlier piston-powered Pilatus P-3, the initial prototype being produced from the existing prototype P-3, principally differing by the substitution of its Lycoming O-435 engine with a Pratt & Whitney PT6A-20 turboprop powerplant. On the 12th of April 1966, the modified prototype performed its maiden flight. However, the PC-7 programme was abruptly shelved following an accident involving the aircraft. The termination of work was reportedly driven by a lack of market interest.
In 1973, it was decided to restart work on the programme; factors for its revival had included the 1973 oil crisis, the launch of the rival Beechcraft T-34C Turbo-Mentor, and the increasing age of the existing trainer aircraft. To support the relaunch, another P-3 was obtained from the Swiss Air Force. After modifications, this aircraft first flew on the 12th of May 1975. Further extensive modifications followed later in the programme, including the adoption of a new one-piece wing complete with integral fuel tanks, along with an altered tailfin and a bubble canopy. The flight test programme came to a close during Autumn 1977.
On August 12th 1978, the first production aircraft made its first flight. On the 5th of December of that year, Switzerland's Federal Office of Civil Aviation (FOCA) issued civil certification for the PC-7; immediately thereafter, initial deliveries of production aircraft commenced to customers in Burma and Bolivia. Over time, sales of the PC-7 generated considerable profits, allowing the company to finance the development of further types of aircraft.
The PC-7 Mk II is a development of the PC-9's airframe and avionics, which was powered by the PC-7's smaller turbine engine, which reportedly achieved lower operating and maintenance costs. This variant was developed at the behest of the South African Air Force (SAAF), who later adopted the type. A batch of 60 PC-7 MK IIs was locally assembled in South Africa using kits supplied by Pilatus for the SAAF; due to political considerations, these aircraft were not fitted with the armament hardpoints. Deliveries to the SAAF took place between late 1994 and 1996.
In addition to Pilatus' own improvement programmes, several third-party companies have independently developed their own upgrades for customer's PC-7. During the late 1990s, Israeli engineering firm Radom began offering a kit of new avionics for the type, which included a new mission computer, a wide-angle head-up display, along with various replacement communications and weapons-delivery systems.
In July 1998, Pilatus announced that it has come to an agreement with American company Western Aircraft for the latter to act as a distributor for the PC-7 across the North American civil aviation market. At this time, there were already five civil-registered PC-7s in operation in North America; Pilatus believed that the region could be a viable market for both remanufactured and newly built examples of the type, which would be priced between $1 million and $2 million respectively. It was recognised that this market was limited, Western Aircraft expected to sell only a few aircraft per year.
| Back to Top |